What Is Hyperthyroidism in Dogs?
Hyperthyroidism in dogs is a rare condition caused by the excessive production of the thyroid hormone, thyroxine. The thyroxine hormone is responsible for controlling a dog’s metabolism and regulating body temperature. Normally, the thyroid gland produces the hormone following stimulation from the pituitary gland. The pituitary gland is the “master gland” in a dog’s body. The thyroid gland is situated in the dog’s neck.
Thyroid hormones usually work to increase chemical processes in the dog’s body. However, when a dog has hyperthyroidism, the excess hormone levels increase the metabolism of the dog—thereby pushing the cells throughout its body into overdrive. This results in a variety of symptoms, including anxiety, weight loss, and diarrhea.
When too little thyroxine is produced, the dog will suffer from hypothyroidism, which means the metabolism slows down. This condition can lead to excessive weight gain, lethargy, and a range of skin and coat problems.

Hyperthyroidism in Dogs Causes
Pet owners that are concerned about this condition may wonder “what causes hyperthyroidism in dogs?” There are two primary causes of hyperthyroidism in dogs.
- Thyroid Carcinoma. This is a cancerous tumor found near the thyroid on the neck. It interferes with the regular functioning of the thyroid gland and causes the excessive secretion of thyroid hormones T3 (triiodothyronine) or T4 (tetraiodothyronine).
- Taking Medication for Hypothyroidism. Hypothyroidism is a more common condition in dogs. To treat this condition, dogs are given a synthetic form of thyroxine. Occasionally, an overcorrection of these hormone levels can cause hyperthyroidism.
Another potential cause of hyperthyroidism is eating a raw food diet. This can occur when the dog consumes raw foods containing large amounts of thyroid hormones. Before switching to a raw food diet, it is important to consult a veterinarian.

Hyperthyroidism in Dogs Symptoms
When a dog’s metabolism increases, many irregularities occur in the systems of its body. The most common symptom of hyperthyroidism is weight loss, even when there is an increased appetite. The following is a comprehensive dog hyperthyroidism symptoms checklist.
- Severe weight loss
- An increase in appetite
- Increased thirst
- Frequent urination
- Diarrhea
- Vomiting
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Excitability
- Depression
- An increased amount of stool
- A fast or erratic heartbeat (tachycardia)
- Problems breathing (dyspnea)
- A lump in the neck where the thyroid gland becomes enlarged
- Heart murmur
In rare cases, untreated hyperthyroidism in dogs can lead to kidney failure. Therefore, it is essential that any dog exhibiting these symptoms be taken to a veterinarian for a full assessment.

What Dog Breeds Are Most Susceptible to Hyperthyroidism?
There are several breeds that are more prone to developing hyperthyroidism.
- Beagle
- Golden Retriever
- Siberian Husky
Hyperthyroidism in Dogs Diagnosis
If any of the signs of hyperthyroidism in dogs are observed, it is essential that a veterinarian is consulted, and an assessment is carried out. The veterinarian will first examine the thyroid gland, which will be enlarged if the dog has hyperthyroidism.
The next step is to conduct blood tests and a urinalysis designed to measure thyroid hormones. The veterinarian will be looking for a high concentration of the thyroid hormone T4 in the blood.
During the early stages of the condition, the dog’s T4 levels will be in the normal range, making diagnosis more challenging. When these blood tests are inconclusive, it is likely that the veterinarian will carry out further tests.
A veterinarian may order general blood work to be carried out as the thyroid problems the dog may be experiencing could be secondary to another illness. A more comprehensive test will identify or rule out such potential causes. General blood tests will identify liver problems and dehydration.
When a lump is present in the neck of the dog, a tissue biopsy will be performed to find out whether the underlying cause is cancer. Further diagnostic imaging tests may be carried out to learn the full extent of a tumor.
A thyroid gland scintigraphy creates a 2D image using radioisotopes. This helps pinpoint the location of any abnormalities in the thyroid tissue. Additionally, echocardiography and thoracic radiography will be used to assess any signs of myocardial disease. A chest X-ray can help to identify pulmonary metastasis.

Hyperthyroidism Treatment in Dogs
Following the assessment of the underlying causes, a veterinarian will advise how to treat hyperthyroidism in dogs.
Where hyperthyroidism is caused by an excessive dose of hypothyroidism medication, the solution will be for the veterinarian to adjust the dosage. When the dose is corrected, the symptoms will usually diminish.
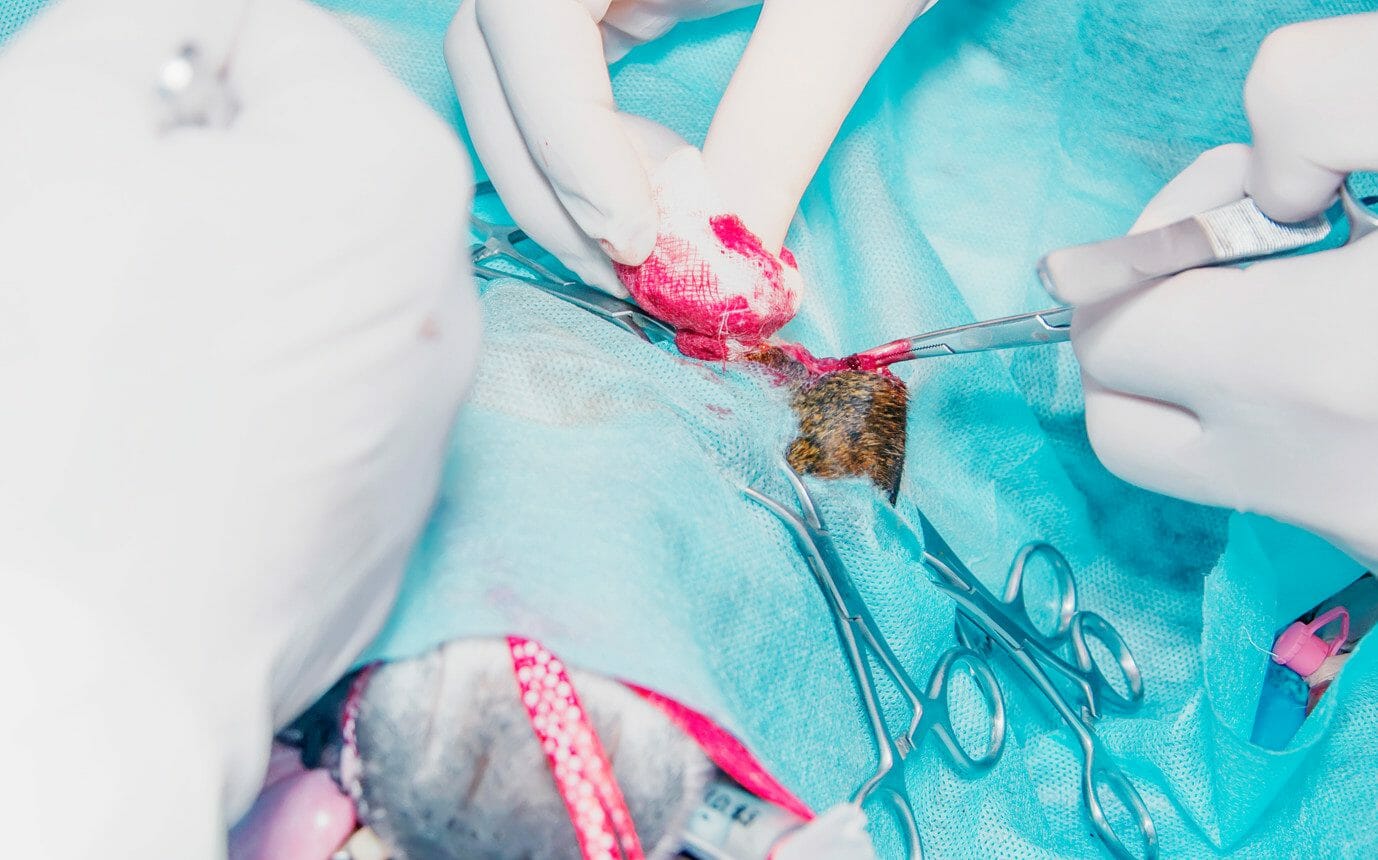
One treatment option is to have the affected thyroid gland surgically removed. This option is only suitable where just one gland is affected. Removing both could lead the dog to develop hypothyroidism. Another issue with surgical removal of the affected gland is that the remaining gland could remain hyperactive.
When the underlying cause is a thyroid tumor, being able to carry out surgery will depend on how invasive the tumor is. Surgery can become more difficult or even impossible when the tumor is too close to the dog’s major arteries and esophagus.
In cases where the position of the tumor is an issue, a portion may be removed, and the rest will be treated with radioactive therapy. The prognosis of such actions will depend on how far into the surrounding tissue the tumor has metastasized.
Once all the major hyperthyroidism symptoms have been resolved, it may be necessary to make modifications to the dog’s diet.
Preventing Hyperthyroidism in Dogs
Owners providing a raw food diet for their dogs should be aware that such a diet may contain head meat, gullets, and neck meat, which have excessive amounts of thyroid hormones. Always consult with a veterinarian before starting such a diet. If a dog has hypothyroidism, owners should watch for the signs of hyperthyroidism to ensure the canine is receiving a suitable medication dosage.
Prognosis for Hyperthyroidism in Dogs
The early detection and treatment of hyperthyroidism in dogs are essential to ensure a full recovery. In instances where the condition is caused by a cancerous tumor on the thyroid gland, the survival of the dog will be dependent on how far the tumor has spread before detection.



